| 产品名称: Ras(Q61L) 蛋白 |
| 货号 10111 |
| 产品全名: Ras Protein Q61L 突变蛋白 |
| 基因符号 GTPase Ras |
| Source: Human, recombinant full length, His6-tag |
| Expression 种属反应性: E. coli |
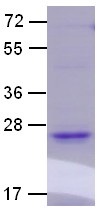
| 分子量: 21 kDa |
| 纯化: >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Introduction: Small GTPases are a super-family of cellular signaling regulators. Ras belongs to the Ras sub-family of GTPases that regulate cell proliferation, cell motility, and gene transcription. GTP binding increases the activity of Ras, and the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP renders it inactive. GTP hydrolysis is aided by GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), while exchange of GDP for GTP is facilitated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). |
| Amino Acid Sequence (1-189, Q61L) |
MTEYKLVVVGAGGVGKSALTIQLIQNHFVDEYDPTIEDSYRKQVVIDGETCLLDILDTAGLEEYSAM
RDQYMRTGEGFLCVFAINNTKSFEDIHQYREQIKRVKDSDDVPMVLVGNKCDLAARTVESRQAQDLA
RSYGIPYIETSAKTRQGVEDAFYTLVREIRQHKLRKLNPPDESGPGCMSCKCVLS |
Properties
|
| Physical Appearance (form): Dissolved in 20mM Tris-HCl, pH8.0, 150mM NaCl. |
| Physical Appearance (form): White or clear |
| Concentration: 3 mg/mL |
| Storage: -80°C |
Preparation Instructions:
Centrifuge the vial before open the cap and reconstitute in water. Adding of 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol or 1 mM DTT into the solution to protect the protein is recommended and using of non-ionic detergents such as n-Dodecyl β-D-maltoside (DoDM) or polyethylene detergents (e.g. C12E10) also help to stabilize the protein. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing after reconstitution. The purity of His-tagged Ras Q61L was determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining. |
References:
1. Chen, H.-J. et al., Neuron 20: 895-904, 1998.
2. Hamdan, F. F. et al., New Eng. J. Med. 360: 599-605, 2009.
3. Oh, J. S. et al., Neuron 33: 151 only, 2002.
4. Rumbaugh, G. et al., Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 103: 4344-4351, 2006.
5. Tomoda, T. et al., Genes Dev. 18: 541-558, 2004.




